On February 12, 2021, The UK Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) published their annual GCP INSPECTIONS METRICS REPORT. This report covered the period from 1 April 2018 to 31 March 2019.
The report provides excellent insight into MHRA’s compliance concerns. In this edition, there were a number of detailed findings related to the Trial Master File.
The report includes findings in three categories:
- Sponsor: 8 inspections, 4 with at least one critical finding, and 7 total critical findings. 2 of these were directly related to the Trial Master File. For one sponsor, this was a major finding at the previous inspection of this organisation and was therefore escalated to a critical finding
- CRO: 11 inspections, 4 with at least one critical finding, and 6 total critical findings. 1 of these was directly related to the Trial Master File.
- Non-Commercial Entity: 11 inspections, 2 with at least one critical finding, and 3 total critical findings. 1 of these was indirectly related to the Trial Master File.
TMF-related observations were also common beyond critical findings. Although MHRA does not provide details, Record Keeping/Essential Documents was actually the most common area of findings, accounting for about 18% of all total findings for sponsor inspections.
The report contained a total of 33 individual observations related to eTMF. When the observations were categorized, a number of trends emerged, which are summarized below (showing only observations that occurred more than once).
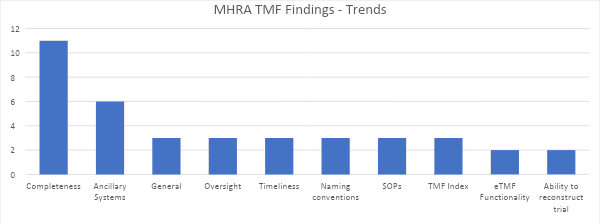
Some important trends include:
- TMF Completeness. Numerous observations related to the completeness of the TMF. In some cases, completeness was lacking because the scope of the TMF did not include all essential documents, especially if not stored in the core eTMF. Other observations could be traced to failure to file required documents and lack of oversight in including completeness. TMF completeness issues are not new or suppressing, but show that some organizations are not taking action based on previous years’ observations.
- Ancillary Systems. This area showed increased focus by MHRA. Observations included failure to define ancillary systems as containing TMF content, lack of control and oversight, and failure to define the system of record in TMF SOPs and indices. As a result, this area is tightly coupled with completeness issues.
- Naming Conventions. Inspectors should be able to rely on consistent naming conventions to identify documents and understand their contents without having to open documents.
For a complete analysis and a set of recommended review actions, see Ennov’s MHRA TMF Inspection Finding Review Checklist available on Ennov Insider. If you’re not already a member, join today for free access to a useful set of white papers, videos and other resources.


